Avocado and Cholesterol Levels - Study Overview
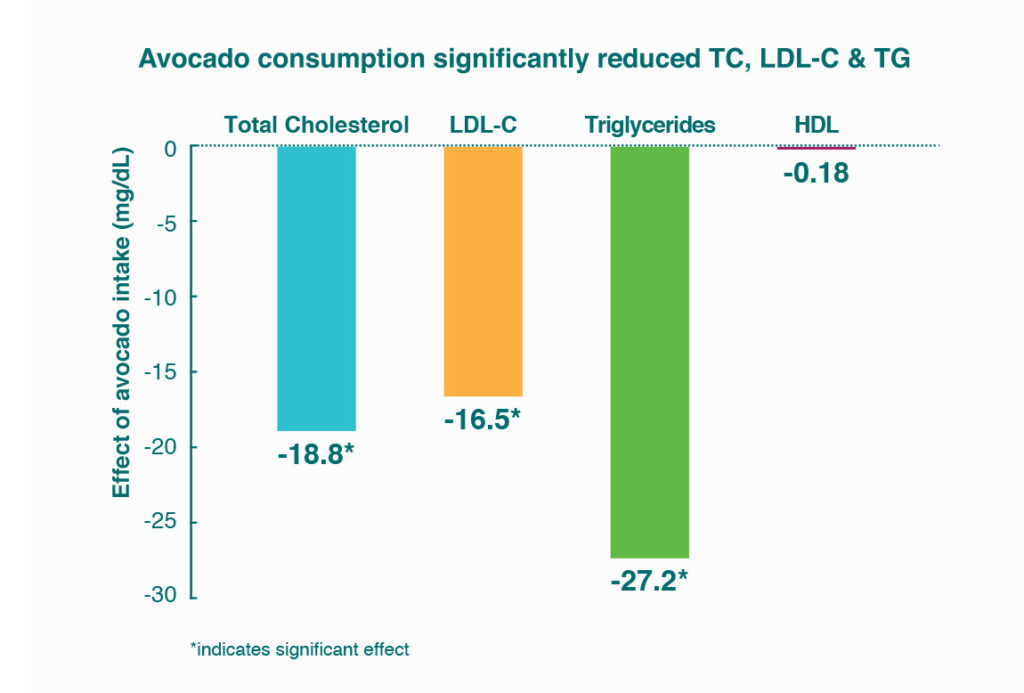
The study conducted by the University of the Pacific and independently funded was published in the Journal of Clinical Lipidology.1 The meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials assessed the impact of avocados on cholesterol levels. Researchers found avocado consumption significantly reduced total cholesterol (TC), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and triglycerides (TG) when avocados were substituted for sources of saturated fat. The optimal amount of avocado and frequency of use needs further evaluation along with the nutritional similarities and differences between other different MUFA sources. Larger trials looking at the impact of avocados on major adverse cardiovascular events are warranted.
Published: Journal of Clinical Lipidology.
Study funded by Hass Avocado Board
Category: Cardiovascular Health
Download Scientific Summary PDF
See Published Study
Key Takeaways and Findings
Avocado consumption reduced TC, LDL-C and TG when substituted for sources of saturated fat. A smaller value is preferable.
Avocado consumption did not impact high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL). A larger value is preferable.
METHOD:
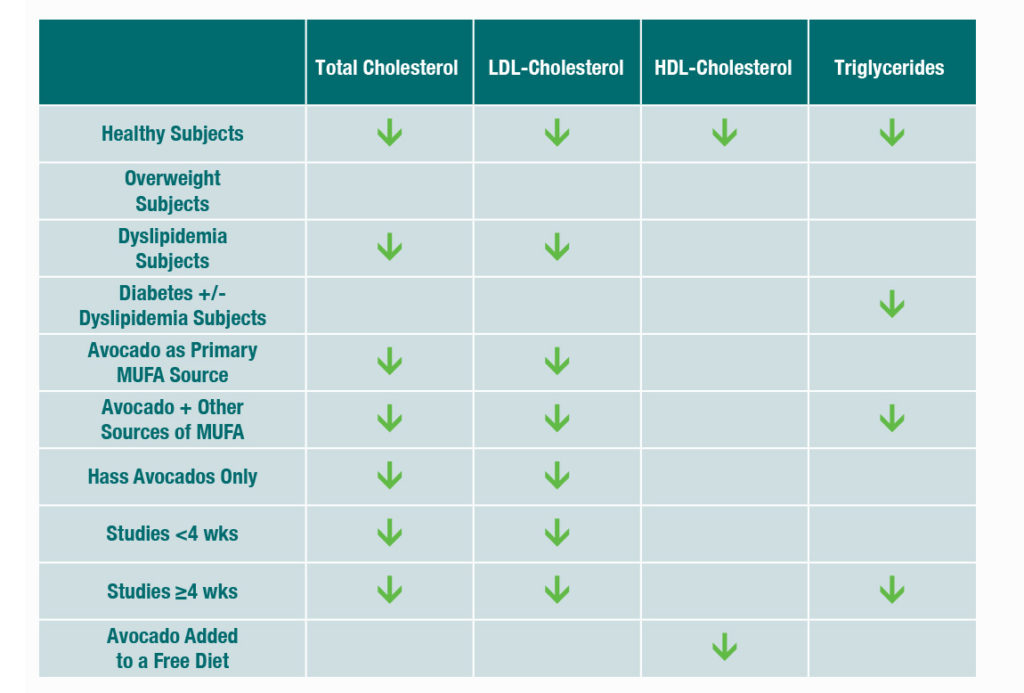
This study conducted a systematic literature review in order to use a statistical technique that combined the results from 229 subjects from 10 independent studies to estimate the overall impact of avocado consumption on cholesterol levels. The study is considered a meta-analysis and systematic review, which is considered the best evidence and an unbiased overview of the body of knowledge on a specific topic.

CONCLUSION:
Based on these findings, researchers concluded that when avocado was substituted for food sources of saturated fat, the swap reduced TC, bad LDL-C and TG levels without adversely impacting good HDL levels. Researchers further recommended individuals substitute dietary fats with avocados rather than simply adding avocados to a free diet. Results drawn from 10 independent studies indicate that avocado intake improves cholesterol levels and researchers indicate that larger trials looking at the impact of avocados on cardiovascular disease are warranted.
The amount of avocado consumed ranged from one half to 1.5 avocados per day. Although half of the trials were conducted with the Hass variety, it is possible that consumption of other varieties also maintains healthy cholesterol levels. Due to weight loss in some studies, it cannot be ruled out that some of the beneficial effects of this study can be attributed to weight loss. Due to small sample size, interpretation of subgroup analyses is limited. For that reason, it is possible that adding free avocados may have health benefits independent of maintaining healthy cholesterol levels, as other endpoints such as weight, BMI, and cholesterol particle size and subclass were not assessed in this study.
FUNDING:
This study was independently supported. Although the Hass Avocado Board (HAB) did not fund this study, HAB has a scientific research pipeline of ongoing clinical studies currently investigating the relationship between fresh avocado consumption and cardiovascular health, weight management and diabetes, and enhanced nutrient absorption. And, based on their nutrient and phytochemical profile, emerging research suggests that fresh avocados may play a positive role in many research areas including skin, eye, joint and cellular health.

Hass Avocado Board Supports Nutrition Research
The Hass Avocado Board (HAB) is a promotion, research and information organization under supervision of the United States Department of Agriculture. HAB has a science research pipeline of ongoing clinical studies investigating the relationship between fresh avocado consumption and weight management and risk factors for cardiovascular disease and diabetes. And, based on their nutrition and phytochemical components, emerging research suggests that avocados may play benefit many emerging areas, including skin, eye, joint and cellular health.
Reference:
1. Peou S, Milliard-Hasting B, Shah SA. Impact of avocado-enriched diets on plasma lipoproteins: A meta-analysis. J Clin Lipidol. 2016 Jan-Feb;10(1):161-71.