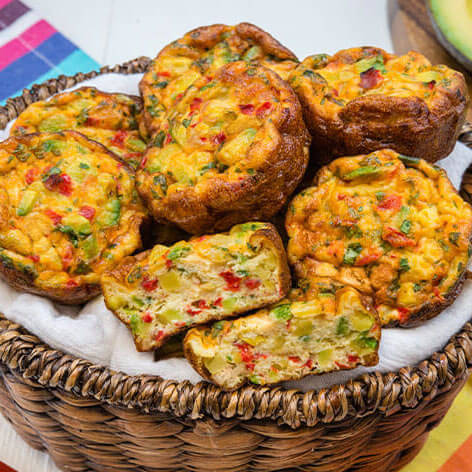
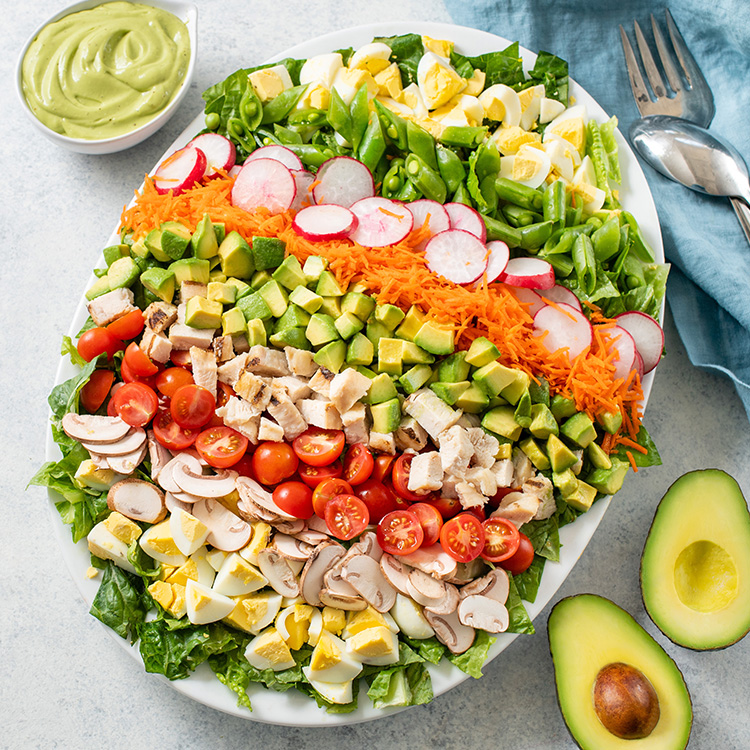
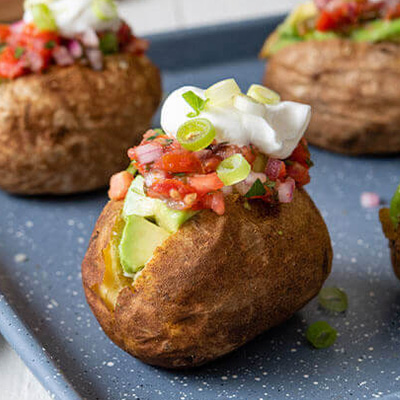
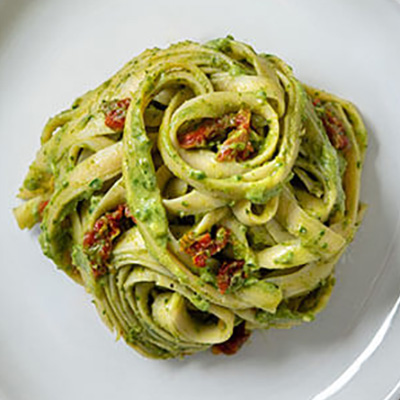
Avocados are celebrated not just for their creamy texture and delicious taste, but also for their impressive health benefits. If you’re looking to improve your heart health, avocados should definitely be on your radar. With 22 essential nutrients and 6 g of good fats per serving, they offer a unique combination of benefits that can support cardiovascular wellness. Let’s explore why avocados are heart-healthy, the nutritional value they provide, the role of good fats, and how to incorporate them into delicious, heart-friendly recipes.
In short, avocados are recognized by the American Heart Association as a heart-healthy food. They’re free of cholesterol, sodium, and sugar, and are low in saturated fat. Plus, just one serving offers 6g of good fats and 3g of fiber, both of which are known for lowering bad cholesterol levels and reducing the risk of heart disease, obesity, and type 2 diabetes.

What Makes Avocado Heart Healthy?
Avocados are a versatile and nutritious addition to any diet, especially for those focused on heart health. Their unique combination of healthy fats, fiber, and essential nutrients makes them an excellent choice for maintaining healthy cholesterol levels, regulating blood pressure, and supporting overall heart function. By incorporating avocados into your meals through simple and delicious recipes, you can enjoy their many benefits while keeping your heart healthy and strong. Whether you’re making a refreshing salad, a nutrient-packed smoothie, or a hearty taco, avocados offer a tasty and beneficial way to boost your heart health. Enjoy your avocados and take a step towards a healthier heart!
What is the Nutritional Value of an Avocado?
Avocados are nutrient-dense fruits, providing a wide array of vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats in each serving. Here’s a breakdown of the key nutrients found in a typical serving of avocado (about one-third of a medium avocado, or 50 grams):
What Makes a Fat “Good” or “Bad”?
Understanding the difference between “good” fats and “bad” fats is crucial for maintaining heart health and overall well-being. Fats are an essential part of our diet, providing energy, supporting cell growth, and helping in the absorption of certain nutrients. However, not all fats have the same effects on our bodies. Here’s a breakdown of what makes a fat “good” or “bad”.
Good Fats:

Monounsaturated Fats (MUFAs)
Sources: Avocados, olive oil, nuts, and seeds.
Benefits: These fats are known for their ability to reduce bad LDL cholesterol levels while increasing good HDL cholesterol levels. This balance helps to lower the risk of heart disease and stroke. MUFAs also have anti-inflammatory properties and can improve insulin sensitivity, which is beneficial for managing type 2 diabetes.

Polyunsaturated Fats (PUFAs)
Sources: Fatty fish (such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines), flaxseeds, walnuts, and sunflower oil.
Benefits: PUFAs include omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which are essential fats that our bodies cannot produce. Omega-3 fatty acids, in particular, are known for their heart-protective properties, including reducing inflammation, lowering triglyceride levels, and supporting overall cardiovascular health. Omega-6 fatty acids, when consumed in moderation and balanced with omega-3s, also play a role in brain function and normal growth and development.
Bad Fats:

Saturated Fats
Sources: Red meat, butter, cheese, and other full-fat dairy products, as well as certain tropical oils like coconut oil and palm oil.
Effects: High intake of saturated fats can raise levels of bad LDL cholesterol in the blood, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke. While not all saturated fats have the same impact, and some may be less harmful than others, it is generally recommended to limit their consumption and replace them with unsaturated fats where possible.

Trans Fats
Sources: Partially hydrogenated oils found in many processed foods, such as baked goods, snack foods, and some margarines.
Effects: Trans fats are particularly harmful because they not only raise bad LDL cholesterol levels but also lower good HDL cholesterol levels. This double impact significantly increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. Due to these adverse effects, many health organizations recommend eliminating trans fats from the diet entirely.
How to Choose the Right Fats:
Read Labels
Check food labels for the types of fats included. Look for products with higher amounts of unsaturated fats and minimal to no trans fats.
Cook Wisely
Use oils high in unsaturated fats, such as olive oil or canola oil, for cooking. Avoid frying and opt for healthier cooking methods like grilling, baking, or steaming.
Balance Your Diet
Incorporate a variety of fat sources, focusing on those rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. Balance omega-6 fatty acid intake with omega-3 sources to maintain a healthy ratio.
Moderation
Even good fats should be consumed in moderation, as all fats are calorie-dense. Portion control can help maintain a healthy weight and support overall health.
By understanding the difference between good and bad fats and making informed dietary choices, you can significantly improve your heart health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Avocados provide 1g of polyunsaturated fat and 5g of monounsaturated fat, making them a perfect example of a heart-healthy fat source that can be easily incorporated into a balanced diet.
Download fresh facts about avocados and good fats
What are the Connections Between Cholesterol and Blood Pressure?
Cholesterol and blood pressure are two critical factors that significantly influence heart health. Although they are distinct conditions, they are interconnected in ways that can impact your cardiovascular system.
Here’s an explanation of how these two elements are related and how they together affect heart health:
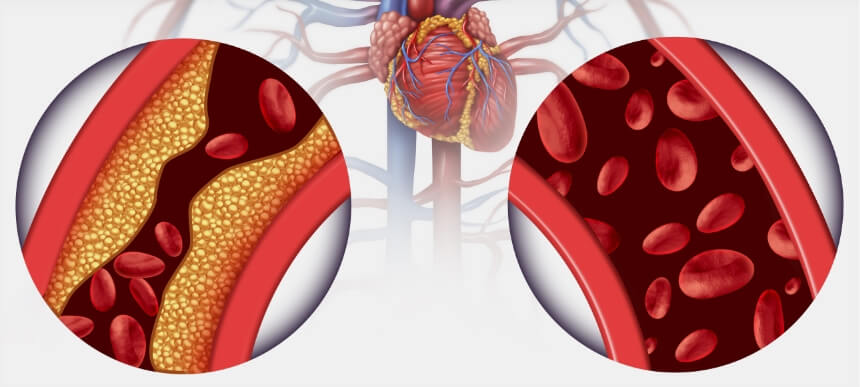
Understanding Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a waxy substance found in your blood. Your body needs cholesterol to build healthy cells, but high levels of cholesterol can increase your risk of heart disease. There are two main types of cholesterol:
Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL): Often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, high levels of LDL can lead to the buildup of plaques in your arteries. These plaques can narrow your arteries, making it difficult for blood to flow through, and increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke.
High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL): Known as “good” cholesterol, HDL helps remove LDL cholesterol from the arteries and transports it back to the liver, where it is processed and eliminated from the body.
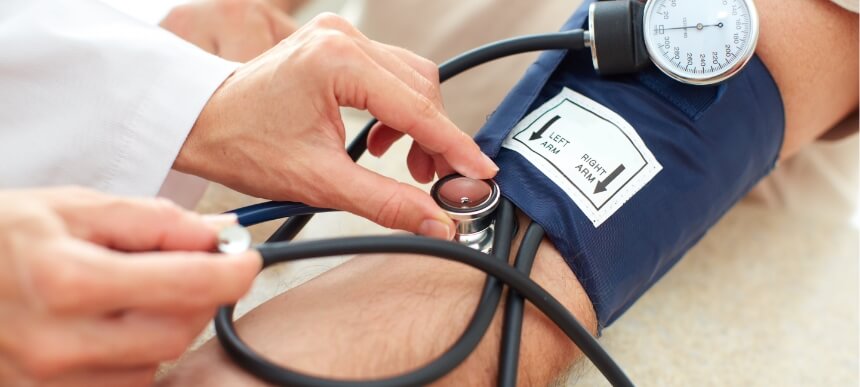
Understanding Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is the force of your blood pushing against the walls of your arteries. High blood pressure, or hypertension, occurs when this force is consistently too high, which can damage your arteries and lead to heart disease. Blood pressure is measured in two numbers:
Diastolic Pressure: The pressure when your heart beats.
High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL): The pressure when your heart rests between beats.
High levels of LDL cholesterol can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries, narrowing them and increasing blood pressure. This plaque buildup can also make arteries stiffer, further elevating blood pressure. Additionally, both high cholesterol and high blood pressure can cause inflammation in the arteries, worsening each other’s effects. Managing both cholesterol levels and blood pressure is crucial for heart health. This includes adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and, if necessary, taking medication as prescribed by a healthcare professional. By addressing both factors, you can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease and maintain overall cardiovascular health.
Following a DASH eating plan is scientifically proven to help lower blood pressure.
Get started with this simple meal plan.
Heart-Healthy Avocado Recipes
Creating a heart-healthy recipe involves choosing ingredients that support cardiovascular health while still being delicious and satisfying.
Here are some key components to consider:
Avocados are perfect for a heart-healthy diet due to their beneficial fats, fiber, and essential nutrients. Love One Today® offers delicious heart-healthy avocado recipes that make it easy to love your heart-friendly diet. From breakfast and savory salads to delightful main dishes and desserts, our recipes help you incorporate this nutritious fruit into your meals effortlessly. Try some of our fan favorites today!













