Fat-soluble vitamins require dietary fat for optimal absorption in the body. These vitamins support immune function, vision, bone health, and blood clotting, but without sufficient fat in your diet, your body may not absorb them properly.
Fat-soluble vitamins include:
- Vitamin A:
You can find this vitamin in carrots, kale, and sweet potatoes - Vitamin D:
Vitamin D is found in fatty fish and fortified dairy. - Vitamin E:
This vitamin is in nuts, greens, and fruits like papaya. - Vitamin K:
This vitamin is in broccoli, spinach, and eggs.

Since avocados provide 5 g of monounsaturated fats per 50 g serving, they can help your digestive system absorb these essential nutrients more efficiently. Whether added to salads, blended into smoothies, or featured in dishes like avocado pumpkin pie or avocado mashed potatoes, avocados help turn nutrient-rich meals into nutrient-absorbing powerhouses. In addition to promoting nutrient absorption, the unsaturated fats in avocados may also help lower blood cholesterol levels and support heart health.
Fat-Soluble Vitamins and Avocados
Not all fats are created equal, and the unsaturated fats in foods like avocados play a key role in helping your body absorb and utilize essential nutrients. These healthy fats are crucial for absorbing fat-soluble vitamins such as A, D, E, and K, ensuring that your body can effectively use them for vital functions like immune support, bone health, and cell growth. In addition to promoting nutrient absorption, the unsaturated fats in avocados may also help lower blood cholesterol levels and support heart health.

What Are Fat-Soluble Vitamins?
Fat-soluble vitamins are a group of vitamins that dissolve in fat and are stored in your body’s liver and fatty tissues for later use. Unlike water-soluble vitamins, which need to be replenished regularly because they are excreted through urine, fat-soluble vitamins can be stored for longer periods. These vitamins—A, D, E, and K—play vital roles in supporting essential functions like immune health, vision, bone strength, and blood clotting. Since they require dietary fats for absorption, consuming foods that contain healthy fats, such as avocados, helps ensure your body can effectively absorb and use these vitamins.

Fat-soluble Vitamins A, K, E, and D
Each fat-soluble vitamin is unique and serves a different purpose in aiding the body. Let’s look at each vitamin and how it helps the body function.

VITAMIN A
Vitamin A, also known as retinol, is a fat-soluble vitamin that plays an essential role in supporting your immune system and promoting overall health. Vitamin A helps by supporting the growth of white blood cells, which help fight infections.
Although you can take a vitamin A supplement, it’s best to prioritize eating foods that naturally contain vitamin A, such as:
- Liver, beef, and fish
- Dairy products
- Squash
- Kale
- Sweet Potato
- Apricots
- Tomato
- Carrots
- Egg Yolks
- Mangos
- Spinach
- Cantaloupe
Some of these foods, like squash, kale, egg yolks, mangos, and spinach, also have other fat-soluble vitamins, making them excellent additions to a nutrient-dense diet.
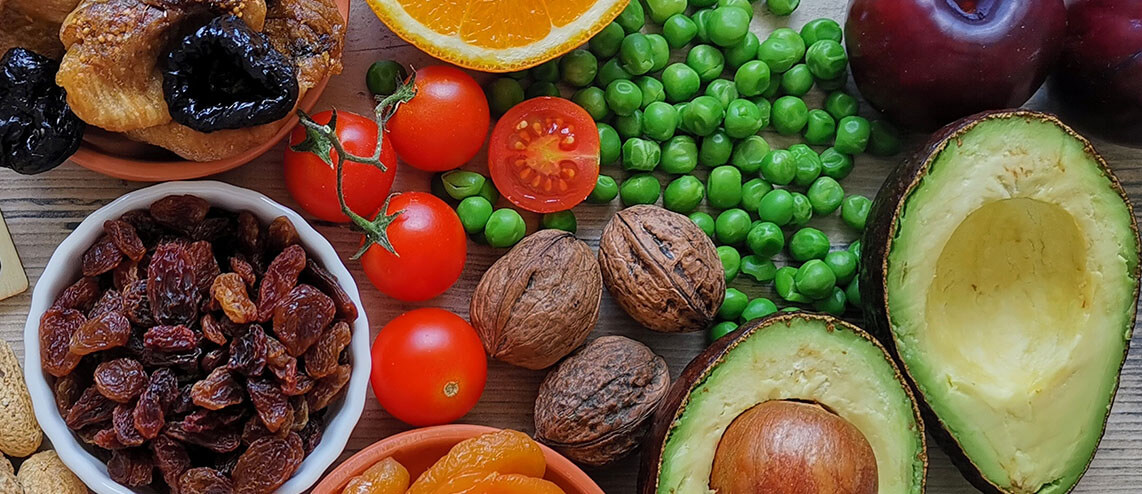

VITAMIN K
As a fat-soluble vitamin, vitamin K’s primary purpose is to clot blood and maintain the integrity of your bones. Vitamin K does this by producing proteins that are essential in the blood clotting process.
To prevent extensive blood clotting, it’s best to prioritize eating foods high in vitamin K, such as:
- Broccoli
- Dark green vegetables (including Brussels sprouts)
- Cauliflower
- Asparagus
- Cabbage
- Cereals
- Dark leafy vegetables
- Fish, liver, beef, and eggs
- Avocados
Broccoli and asparagus also feature vitamin E, another fat-soluble vitamin you need in your diet.
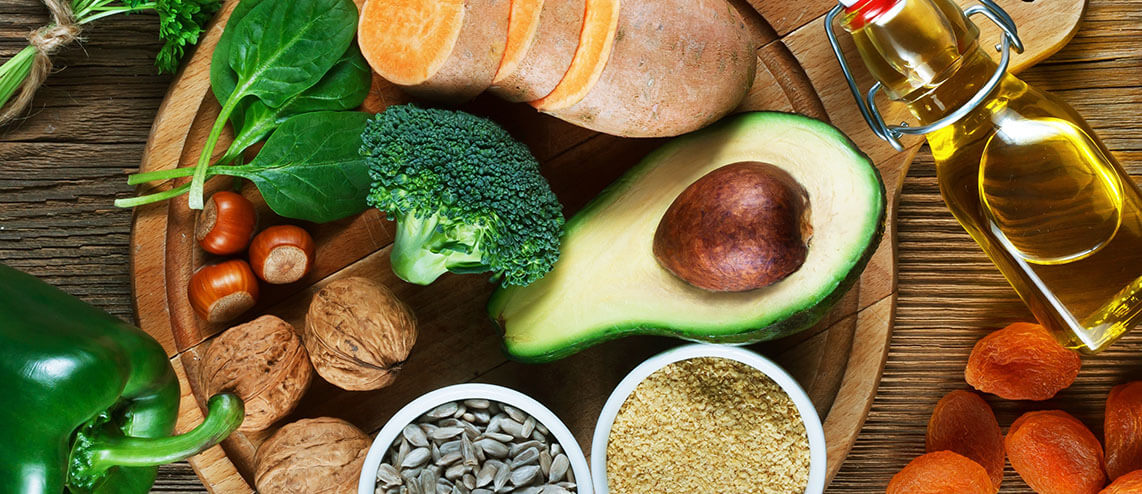

VITAMIN E
Like vitamins A and K, vitamin E is crucial for supporting your immune system. Known as tocopherol, vitamin E primarily aids in the formation of red blood cells and acts as a powerful antioxidant. It helps protect cells from damage caused by free radicals, which are linked to cancer, heart disease, and other age-related conditions.
Vitamin E naturally occurs in plenty of food sources, including:
- Avocado
- Seeds and nuts
- Dark green vegetables
- Oils
- Papaya
- Wheat germ
Avocados are an excellent choice because one serving not only provides 7% of vitamin E but also provides 6 grams of healthy fats, which help your body absorb this and other fat-soluble vitamins more effectively.
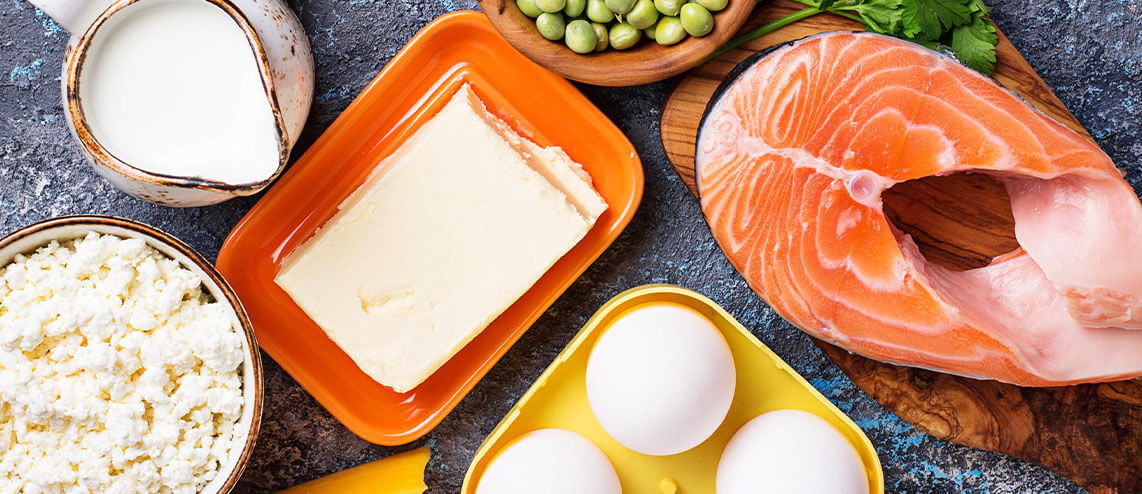

VITAMIN D
Vitamin D, or calciferol, plays a crucial role in many essential bodily functions. It aids in the absorption of calcium, which is important for maintaining healthy teeth and bones. Additionally, it supports cell growth, helps regulate glucose levels, and strengthens the immune system.
Unlike other vitamins, vitamin D can be produced by your body when exposed to sunlight. UV rays from the sun trigger vitamin D synthesis in your skin. You can also get vitamin D from natural food sources such as:
- Fortified milk and dairy products like cheese and yogurt
- Fatty fish, like salmon
While increasing your daily exposure to sunlight can boost vitamin D levels, it’s important to balance sun exposure with skin protection. Using sunscreen reduces the risk of UV-related skin damage, and short periods of sun exposure can still help maintain vitamin D levels without increasing your skin cancer risk.
How Good Fats Help You Absorb More Vitamins
Fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K) require dietary fat to be effectively absorbed by the body. These vitamins dissolve in fat during digestion, allowing them to enter the bloodstream and perform critical functions like supporting immune health, vision, and bone strength. Without enough fat in your diet, even if you consume sufficient amounts of these vitamins, your body may not fully absorb them, potentially leading to deficiencies over time.
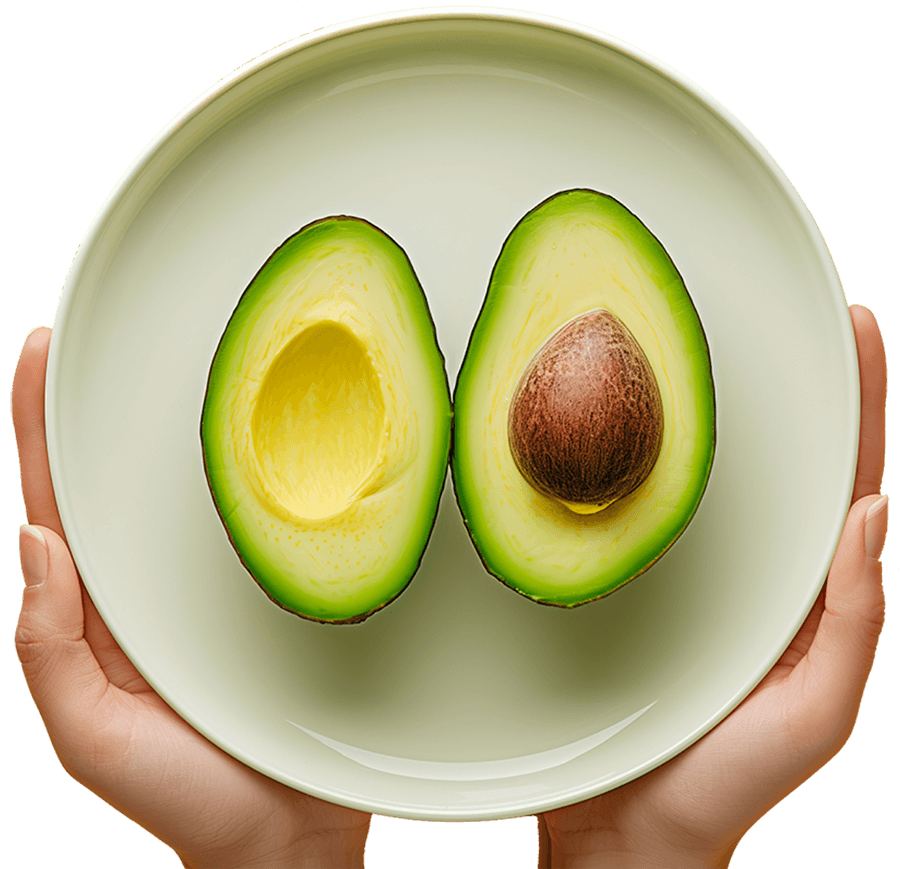

The Good Fats In Avocados
Avocados provide 5 grams of monounsaturated fats per serving, which not only promote heart health by lowering LDL (“bad”) cholesterol and raising HDL (“good”) cholesterol, but also play a crucial role in enhancing the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. Unlike foods high in saturated fats, which can increase the risk of heart disease, the healthy fats in avocados support better nutrient uptake.
Adding avocados to your diet may ensure that your body fully absorbs and utilizes essential vitamins like A, D, E, and K. Whether eaten with salads, in smoothies, or as part of a balanced meal, avocados can act as a nutrient booster, improving the bioavailability (easy and quick absorption) of these important vitamins. This makes avocados an excellent addition to meals that are rich in these vitamins, helping you maximize their health benefits for immune support, bone health, and cell growth.





